Vitamin D promotes bone integrity and maintains calcium homeostasis in the body therefore, acts as a vital micronutrient. Vitamin D is primarily obtained from sunlight whereas fish, mushroom and margarine also serve as important dietary sources. Despite the availability of these sources, vitamin D deficiency is increasing across the globe. Older population is at higher risk of vitamin D deficiency because of reduced synthesis and dietary consumption of vitamin D.
Apart from skeletal growth, vitamin D also plays important
role in brain development. Recent studies revealed that deficiency of vitamin D
is related to cognitive loss, dementia, depression and Parkinson’s disease (1).
Dementia
Decreased levels of vitamin D are commonly observed in cognitively
impaired older individuals (> 65 years of age). Similarly, a meta-analysis
concluded that vitamin D deficiency (< 25 nmol/l) increases the chances of
dementia in adults and elderly population (2).
Vitamin D3 receptor is shown to decrease the amount of toxic peptide (that
causes memory impairment) in the brain therefore, serves as a potential target
for the treatment of dementia (3).
Depression
Several studies reported the association between vitamin D
deficiency and depression. Low levels of vitamin D can cause structural changes
in the hippocampus (brain region involved in memory formation) that lead to
behavioral differences (4).
Calcium levels are important to maintain normal function of
neurons (brain cells) and reduced calcium levels are reported in depression.
Vitamin D acts as the regulator of calcium therefore, alterations in the
vitamin D levels may mediate changes in the neurons that ultimately lead to
depression related symptoms (5).
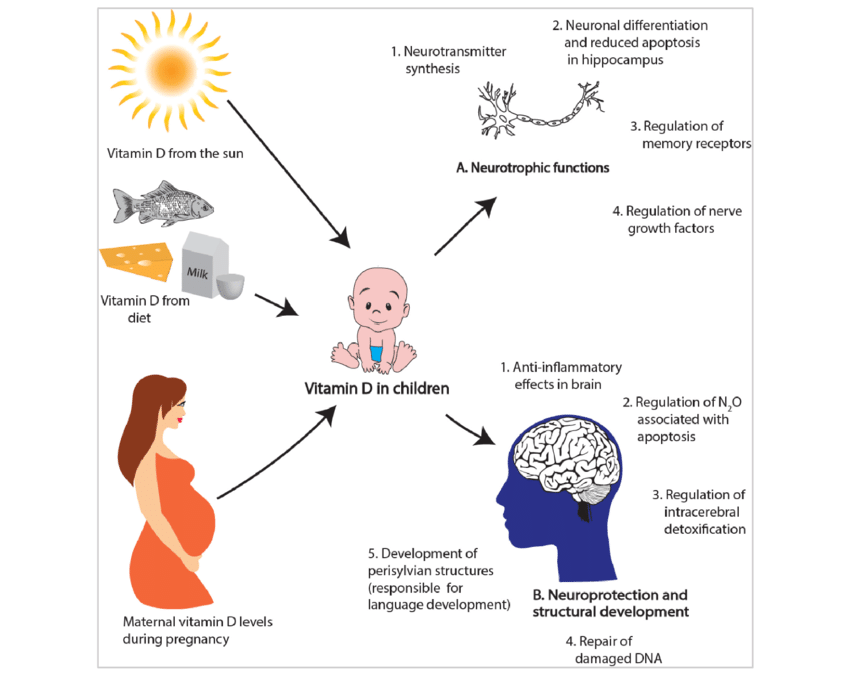
Neuronal development
Normal levels of vitamin D are required for proper brain
development and vitamin D deficiency leads to various developmental disorders. Vitamin
D deficiency is prevalent among pregnant women and this deficiency causes hypoxic-ischemic
brain injury (death of brain cells due to inadequate oxygen supply) in babies (6). Moreover,
insufficient vitamin D concentration during pregnancy is linked to memory and
learning disabilities in children (7).
Parkinson’s disease
Parkinson’s disease is characterized by uncontrolled movement
of limbs in older age. It is caused by reduction in dopamine levels in the
brain. Studies showed that vitamin D affects the dopamine pathway and thereby
contributes to the progression of Parkinson’s disease (8).
Conclusion
Vitamin D plays critical role in neurodevelopment, learning
and memory, depression, Parkinson’s disease and maintenance of calcium homeostasis.
As vitamin D deficiency is related to various neurological disorders therefore,
vitamin D supplementation may treat these devastating diseases. The role of vitamin
D supplementation in brain function will be discussed in upcoming articles so,
stay connected!
References
1.https://www.cureus.com/articles/13567-the-role-of-vitamin-d-in-brain-health-a-mini-literature-review
2.https://bmcgeriatr.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12877-016-0405-0
3.https://www.jneurosci.org/content/34/21/7091
4.https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnmol.2015.00058/full
5.https://pharmrev.aspetjournals.org/content/69/2/80
6.https://www.karger.com/Article/FullText/486819
7.https://joe.bioscientifica.com/view/journals/joe/237/2/JOE-18-0008.xml
8.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S008367291500059X?via%3Dihub








2 Comments
Well explained and informative
ReplyDeleteThank you so much :)
Delete